INTRODUCTION
Testicular lymphoma accounts for <5% of all testicular neoplasms and 1-2% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). Historically, outcomes for testicular lymphoma have generally been inferior to systemic diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with a higher incidence of central nervous system (CNS) relapse. Although intrathecal methotrexate is currently considered standard of care for testicular lymphoma, there has been significant debate about its efficacy in preventing CNS relapse. Due to the rarity of testicular lymphoma, prospective data in this field is lacking. Our study aims to examine treatment practices and outcomes for all newly diagnosed patients with testicular lymphoma in a large tertiary centre in Australia since the introduction of rituximab.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective review of all patients diagnosed with primary testicular lymphoma (PTL) between 2003 and 2019 at the Princess Alexandra Hospital, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (Human Research Ethics Approval: LNR/2019/QMS/56644).
RESULTS
During this period, 18 patients were diagnosed with PTL; all patients had DLBCL histology. The median follow-up period for living patients was 6.5 years (range 1.3-13.4 years).
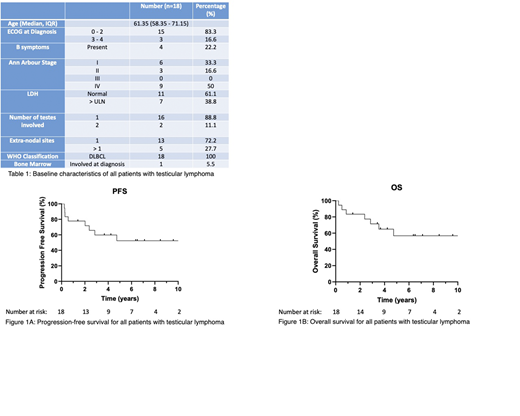
The median age was 61.3 years (interquartile range: 58.3 - 71.1 years). All patients were HIV negative. The majority of patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score of zero (n = 13; 72.2%) with no B symptoms (n = 14; 77.7%) and a normal LDH (n = 11; 61.1%). 50% of patients had Stage IV disease (Table 1).
17 patients (94.4%) underwent an orchidectomy (unilateral: 16, bilateral: 1) at diagnosis. Following on, as first-line systemic therapy, 14 patients (77.7%) received R-CHOP chemotherapy. Other regimens used were CHOP (n=1), modified HyperCVAD (n=1), R-HyperCVAD (n=1) and R-CVP (n=1). 17 patients (94.4%) received CNS prophylaxis with intrathecal chemotherapy; one patient declined intrathecal therapy and was given high dose intravenous methotrexate instead. 15 (83.3%) patients received loco-regional radiation therapy.
Outcomes to first-line treatment were: 13 patients (72.2%) achieved complete remission (CR); one patient (5.5%) achieved partial remission (PR) (Deauville score 4 on interim PET assessment, prompting escalation to salvage therapy); three patients (16.6%) had progressive disease (and were subsequently managed with salvage chemotherapy) and one patient elected for palliation after a single cycle of R-CVP. Among the four patients who received salvage therapy, two patients (50%) achieved CR and two patients had progressive disease and were palliated.
Among the 15 patients who achieved CR (n=13 R-CHOP; n=2 salvage chemotherapy), two patients relapsed, and both had CNS involvement (n=1 CNS only relapse; n=1 CNS and systemic relapse). Despite intrathecal prophylaxis, the CNS relapse rate was 12% (n=2/17).
Of note, the patient who did not receive intrathecal chemotherapy remained in CR at the date of last follow-up. In total, there were seven deaths. The causes of death were: lymphoma (n=4), treatment-related mortality (n=2) and other (n=1; due to aspiration pneumonia after stroke).
The 2-year and 5-year progression free survival (PFS) rates were 77.8% and 52.4%, respectively (Figure 1A). The 2-year and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 83.3% and 56.8%, respectively (Figure 1B).
CONCLUSION
With the practice of R-CHOP, intrathecal prophylaxis for CNS disease and loco-regional radiation therapy, our outcomes are comparable to the literature (5y OS ~50%). Despite intrathecal prophylaxis, our CNS relapse rate was 12%. Better strategies are required to improve the control of systemic disease and reduce the incidence of CNS relapse in patients with testicular lymphoma.
Mollee:Janssen:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding;BMS/Celgene:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Amgen:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Takeda:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Pfizer:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Caelum:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal